In today's interconnected world, efficient data transfer between applications is crucial for smooth operations. Whether it's processing large volumes of requests or orchestrating tasks across distributed systems, having a reliable message broker is essential. RabbitMQ, an open-source message broker, provides a robust solution for building scalable and decoupled applications.
This comprehensive guide will explore leveraging RabbitMQ with C# and .NET to build resilient and flexible messaging systems. From installation to advanced message routing techniques, we'll cover everything you need to know to get started with RabbitMQ.
RabbitMQ is a powerful message broker that facilitates communication between different components of an application. It implements the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP), providing a standardized way for applications to exchange messages. With RabbitMQ, you can decouple your application components, making them more resilient to failures and more accessible to scale.
- Cross-platform Compatibility: RabbitMQ runs on multiple platforms, including Windows and Linux, making it suitable for various environments.
- Language Agnostic: It supports multiple programming languages, allowing you to build applications in your language of choice.
- Persistence Options: RabbitMQ offers in-memory and disk-based message storage options, giving you flexibility in managing message durability.
- Scalability: With support for clustering and high availability, RabbitMQ can handle large volumes of messages and scale horizontally as your application grows.
Before using RabbitMQ, we need to install the Erlang runtime and RabbitMQ server. Follow these steps to install RabbitMQ on your system:
- Download the latest Erlang runtime from erlang.org and install it on your machine.
- Download the latest RabbitMQ server release from rabbitmq.com and unzip the folder to a location on your hard drive.
- Set the
ERLANG_HOMEenvironment variable to the Erlang installation directory. For example:setx ERLANG_HOME "C:\Program Files\erl10.6" - Install RabbitMQ as a Windows service by running the following commands in a console:
rabbitmq-service /install rabbitmq-service /enable rabbitmq-service /start
After installing RabbitMQ, you can use the rabbitmqctl command-line tool to manage the server. Start by ensuring that the server is running:
rabbitmqctl statusYou can secure your RabbitMQ instance by creating a new user with limited permissions and removing the default guest user:
rabbitmqctl add_user myuser mypassword
rabbitmqctl set_permissions myuser ".*" ".*" ".*"
rabbitmqctl delete_user guestAccessing RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ Enable Web Management Plugin
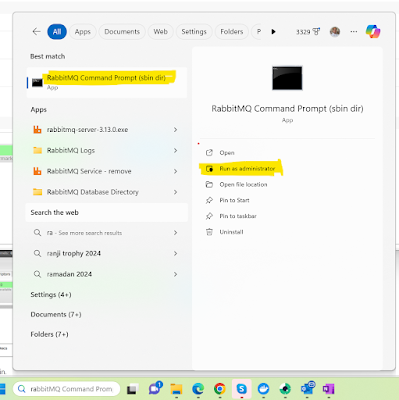
To enable a RabbitMQ web management plugin on Windows, we need to start the RabbitMQ Command Prompt with administrator privileges, enter the command “rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management,” and execute it.
After executing the above web management command, the web management plugins will be enabled, and the enabled list will be shown.
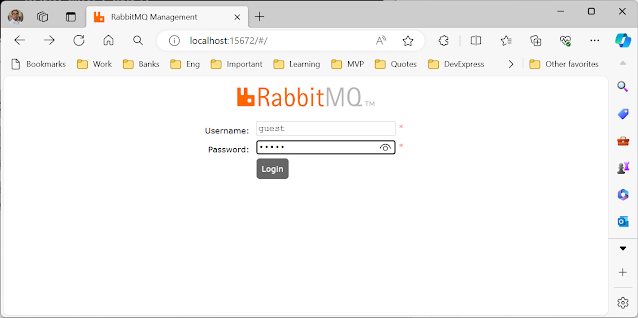
After starting the RabbitMQ Web Management Plugin, enter the following URL in your browser and click 'enter' to open the web management plugin.
http://localhost:15672
After opening the localhost URL in the browser, it will ask you for credentials to access the web management plugin.
To access the RabbitMQ web management dashboard, use the default username and password “guest” (Username: “guest” | Password: “guest”).
After logging in with the default credentials, you will see an overview screen.
Working with RabbitMQ in .NET
Let's integrate RabbitMQ with our .NET applications using the RabbitMQ .NET client library and C#.
To establish a connection to RabbitMQ from a .NET application, we'll need to configure a connection factory:
var connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory
{
HostName = "localhost",
UserName = "myuser",
Password = "mypassword"
};
using (var connection = connectionFactory.CreateConnection())
{
// Create and configure channel
}RabbitMQ uses exchanges and queues to route messages between producers and consumers. Let's create an exchange and a queue and bind them together:
using (var model = connection.CreateModel())
{
// Declare exchange
model.ExchangeDeclare("MyExchange", ExchangeType.Fanout, true);
// Declare queue
model.QueueDeclare("MyQueue", true);
// Bind queue to exchange
model.QueueBind("MyQueue", "MyExchange", "", false, null);
}Now that we have our exchange and queue set up, let's publish a message to the exchange and consume it from the queue:
// Publish message
string message = "Hello, RabbitMQ!";
var body = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(message);
model.BasicPublish("MyExchange", "", null, body);
// Consume message
var consumer = new EventingBasicConsumer(model);
consumer.Received += (sender, args) =>
{
var messageBody = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(args.Body.ToArray());
Console.WriteLine($"Received message: {messageBody}");
};
model.BasicConsume("MyQueue", true, consumer);RabbitMQ offers impressive performance, even under heavy loads. By optimizing message delivery and consumption, you can achieve high throughput and low latency. You can experiment with different configurations and message persistence options to find the best setup for your use case.
In this guide, we've explored the fundamentals of RabbitMQ and demonstrated how to integrate it with C# and .NET applications. By leveraging RabbitMQ's powerful features, you can build robust and scalable messaging systems that meet the needs of your application. You can experiment with different exchange types, message routing strategies, and deployment configurations to unlock the full potential of RabbitMQ in your projects.